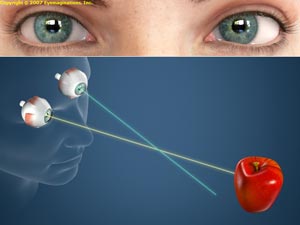
The brain and the eye work together to produce vision. Light enters the eye and is changed into nerve signals that travel along the optic nerve to the brain. Amblyopia is the medical term used when the vision in one of the eyes is reduced because the eye and the brain are not working together properly. The eye itself looks normal, but it is not being used normally because the brain is favoring the other eye. This condition is also sometimes called lazy eye.
How common is amblyopia?
Amblyopia is the most common cause of visual impairment in childhood. The condition affects approximately 2 to 3 out of every 100 children. Unless it is successfully treated in early childhood, amblyopia usually persists into adulthood, and is the most common cause of monocular (one eye) visual impairment among children and young and middle-aged adults.
What causes amblyopia?
Amblyopia may be caused by any condition that affects normal visual development or use of the eyes. Amblyopia can be caused by strabismus, an imbalance in the positioning of the two eyes. Strabismus can cause the eyes to cross in (esotropia) or turn out (exotropia). Sometimes amblyopia is caused when one eye is more nearsighted, farsighted, or astigmatic than the other eye. Occasionally, amblyopia is caused by other eye conditions such as cataract.
How is amblyopia treated in children?
Amblyopia treatment is most effective when done early in the child’s life, usually before age 7. Treating amblyopia involves making the child use the eye with the reduced vision (weaker eye). Currently, there are two ways used to do this:
- Atropine
A drop of a drug called atropine is placed in the stronger eye once a day to temporarily blur the vision so that the child will prefer to use the eye with amblyopia. Treatment with atropine also stimulates vision in the weaker eye and helps the part of the brain that manages vision develop more completely.
- Patching
An opaque, adhesive patch is worn over the stronger eye for weeks to months. This therapy forces the child to use the eye with amblyopia. Patching stimulates vision in the weaker eye and helps the part of the brain that manages vision develop more completely.
Can amblyopia be treated in adults?
During the first six to nine years of life, the visual system develops very rapidly. Complicated connections between the eye and the brain are created. We do not yet have the technology to create these eye-to-brain connections in older children and adults.
Source: National Eye Institute, National Insititues of Health.