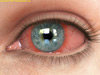
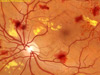
Anterior uveitis is an inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, which includes the iris (colored part of the eye) and adjacent tissue, known as the ciliary body. If untreated, it can cause permanent damage and loss of vision from the development of glaucoma, cataract or retinal edema. It usually responds well to treatment; however, there may be a tendency for the condition to recur.
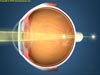
Astigmatism is a condition that causes blurred vision due to the irregular shape of the cornea or the lens inside the eye. The cornea and lens are primarily responsible for properly focusing light entering your eyes allowing you to see things clearly. The curvature of the cornea and lens causes light entering the eye to be bent in order to focus it precisely on the retina at the back of the eye. In astigmatism, the surface of the cornea or lens has a somewhat different curvature in one direction than another.
The brain and the eye work together to produce vision. Light enters the eye and is changed into nerve signals that travel along the optic nerve to the brain. Amblyopia is the medical term used when the vision in one of the eyes is reduced because the eye and the brain are not working together properly. The eye itself looks normal, but it is not being used normally because the brain is favoring the other eye. This condition is also sometimes called lazy eye.
Read more
Blepharitis is the most common inflammation of the eyelids. It may be asymptomatic or can cause irritation, burning, and redness of the lids or conjunctiva. Each person has bacteria present on the surface of their skin and most people will never be bothered by it. This same bacteria on certain individuals tends to thrive at the base of the eyelashes. Irritation may result from the overactivity of the nearby oil glands causing scales and particles to form along the lashes and eyelid margins.
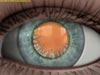
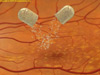
A cataract starts out small. It has little effect on vision at first. You may notice that your vision is blurred a little, like looking through a cloudy piece of glass.
A cataract may make light from the sun or a lamp seem too bright, causing a glare. Or, you may notice when you drive at night that the oncoming headlights cause more glare than before. Also, colors may not appear as bright to you as they once did.
As the cataract gets bigger and clouds more of the lens (some doctors use the term, “ripens”), you will find it harder to read and do other normal tasks. The word “cataract” means waterfall. For people with a ripe cataract, it is like trying to see through a waterfall.
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition occurring in persons with diabetes, which causes progressive damage to the retina, the light sensitive lining at the back of the eye. It is a serious sight-threatening complication of diabetes. Diabetes is a disease that interferes with the body’s ability to use and store sugar, which can cause many health problems. Too much sugar in the blood can cause damage throughout the body, including the eyes.
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that can damage the eye’s optic nerve and result in vision loss and blindness. However, with early treatment, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss. Glaucoma treatments include medicines, laser trabeculoplasty, conventional surgery, or a combination of any of these. While these treatments may save remaining vision, they do not improve sight already lost from glaucoma.
AMD is a common eye disease associated with aging that gradually destroys sharp, central vision. Central vision is needed for seeing objects clearly and for common daily tasks such as reading and driving. In some people, AMD advances so slowly that it will have little effect on their vision as they age. But in others, the disease progresses faster and may lead to a loss of vision in one or both eyes.
For more information on eye conditions, visit American Academy of Ophthalmology EyeSmart.